We Aim To Creat Value For All Customers, And Provide Good-quality
And Good-price Products For All Customers
We Aim To Creat Value For All Customers, And Provide Good-quality
And Good-price Products For All Customers

The transistor's finction is to amplify an electric current.
Many different kinds of transistors are used in analog circuits, for different reasons. This is not the case for digital circuits. In a digital circuit, only two values matter; on or off. The amplification abilitiy of a transistor is not relevant in a digital circuit. In many cases, a circuit is built with integrated circuits(ICs).
Transistors are often used in digital circuits as buffers to protect ICs. For example, when powering an electromagnetic switch (called a 'relay'), or when controlling a light emitting diode. (In my case.)
Two different symbols are used for the transistor.
PNP type ![]() and NPN type
and NPN type ![]()
The name (standard part number) of the transistor, as well as the type and the way it is used is shown below.
When the power supply is the side of the positive (plus), the NPN type is easy to use. | 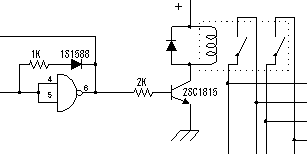 |
![]() Appearance of the Transistor
Appearance of the Transistor
The outward appearance of the transistor varies. Here, two kinds are shown.
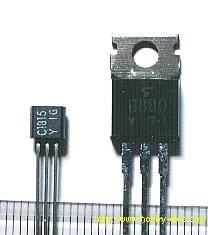
On the left in the photograph is a 2SC1815 transistor, which is good for use in a digital circuit. They are inexpensive when I buy them in quantity. In Japan it costs 2,000 yen for a pack of 200 pieces. (About 10 US cents/piece in 1998)
On the right is a device which is used when a large current is to be handled. Its part number is 2SD880.
The electrical characteristics of each is as follows.
| Item | 2SC1815 | 2SD880 |
|---|---|---|
| VCEO(V) | 50 | 60 |
| IC(mA) | 150 | 3A |
| PC(mW) | 400 | 30W |
| hFE | 70 - 700 | 60 - 300 |
| fT(MHz) | 80 | 3 |
| | : | The maximum voltage that can be handled across the collector(C) and emitter(E) when the base(B) is open. (Not connected) (It may be shown as VCE) |
| | : | The maximum collector(C) current. |
| | : | Maximum collector(C) loss that continuously can cause it consumed at surroundings temperature (Ta)=25°C (no radiator) |
| | : | The current gain to DC at the emitter(E). (IC/IB) |
| | : | The maximum DC switching frequency. (the transision frequency) |
![]() Component Lead of the Transistor
Component Lead of the Transistor
Because the component leads differ between kinds of transistors,
you need to confirm the leads with a datasheet, etc.
![]()
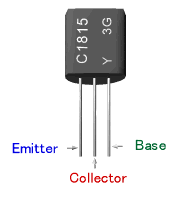
Example of 2SC1815 transistor
Part number is printed on the flat face of the transistor, and indicates the front.
Right side : Base
Center : Collector
Left side : Emitter
![]()
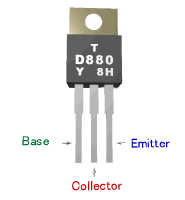
Example of 2SD880 transistor
Part number is printed on the flat face of the transistor, and indicates the front.
Right side : Emitter
Center : Collector
Left side : Base
2SC1815 is opposite.
